Gulletta, Gianpaolo, Eliana Costa e Silva, Wolfram Erlhagen, Ruud Meulenbroek, Maria Fernanda Pires Costa, and Estela Bicho. “A Human-like Upper-Limb Motion Planner: Generating Naturalistic Movements for Humanoid Robots.” International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, (March 2021). https://doi.org/10.1177/1729881421998585. As robots are starting to become part of our daily lives, they must be able to cooperate in … Read More “JournalClub: A Human-like Upper-limb Motion Planner: Generating naturalistic movements for humanoid robots” »
Tag: journalClub
Gulletta, Gianpaolo, et al. “Human-Like Arm Motion Generation: A Review.” Robotics, vol. 9, no. 4, Dec. 2020, p. 102, doi:10.3390/robotics9040102. In the last decade, the objectives outlined by the needs of personal robotics have led to the rise of new biologically-inspired techniques for arm motion planning. This paper presents a literature review of the most … Read More “JournalClub: Human-Like Arm Motion Generation: A Review” »
In my current project I encountered a stumbling block: inefficient/insufficient exploration. While not really useful as a solution to my problem I finally read this paper I had wanted to for a while. Here is the abstract: Yuri Burda*, Harrison Edwards*, Oleg Klimov (all OpenAI), Amos Storkey (Univ. of Edinburgh) *main authors We introduce an … Read More “JournalClub: Exploration by Random Network Distillation” »
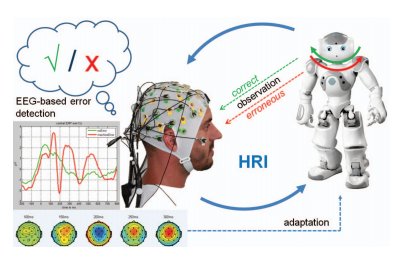
Validating appropriateness and naturalness of human-robot interaction (HRI) is commonly performed by taking subjective measures from human interaction partners, e.g. questionnaire ratings. Although these measures can be of high value for robot designers, they are very sensitive and can be inaccurate and/or biased. In this paper we propose and validate a neuro-based method for objectively … Read More “JournalClub: A neuro-based method for detecting context-dependent erroneous robot action” »
Brain–machine interfaces (BMIs) are promising devices that can be used as neuroprostheses by severely disabled individuals. Brain surface electroencephalograms (electrocorticograms, ECoGs) can provide input signals that can then be decoded to enable communication with others and to control intelligent prostheses and home electronics. However, conventional systems use wired ECoG recordings. Therefore, the development of wireless … Read More “JournalClub: A Fully Implantable Wireless ECoG 128Channel Recording Device for Human Brain–Machine Interfaces” »
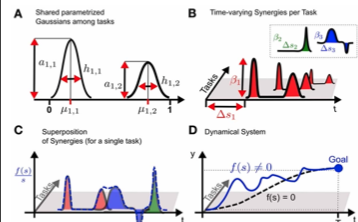
A salient feature of human motor skill learning is the ability to exploit similarities across related tasks. In biological motor control, it has been hypothesized that muscle synergies, coherent activations of groups of muscles, allow for exploiting shared knowledge. Recent studies have shown that a rich set of complex motor skills can be generated by … Read More “JournalClub: Learned parametrized dynamic movement primitives with shared synergies for controlling robotic and musculoskeletal systems” »
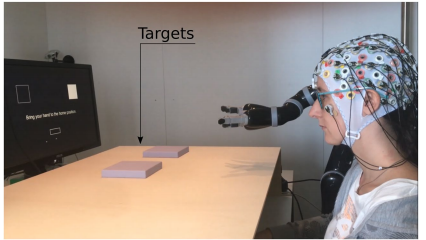
Error-related potentials (ErrPs) are the neural signature of error processing. Therefore, the detectionof ErrPs is an intuitive approach to improve the performance of brain-computer interfaces (BCIs). The incorporation of ErrPs in discrete BCIs is well established but the study of asynchronous detection of ErrPs is still in its early stages. Here we show the feasibility … Read More “JournalClub: Online asynchronous decoding of error-related potentials during the continuous control of a robot” »
Movement primitives are elementary motion units and can be combined sequentially or simultaneously to compose more complex movement sequences. A movement primitive timeseries consist of a sequence of motion phases. This progression through a set of motion phases can be modeled by Hidden Markov Models (HMMs). HMMs are stochastic processes that model time series data … Read More “JournalClub: Modeling Movement Primitives with Hidden Markov Models for Robotic and Biomedical Applications” »
This work has been conducted in the context of pattern-recognition-based control strategies for electromyographic prostheses. It focuses on the conceptual design, implementation and validation of learning techniques based on the k-nearest neighbour (kNN) scheme for gesture recognition. After theoretical considerations and the identification of the topic within the contexts of prosthetic control, biomedical signals — … Read More “JournalClub: Nearest-Neighbour-Based Learning Techniques for Proportional Myocontrol in Prosthetics” »
Presented on 10.06.2020 by Aline Xavier Fidencio