This report describes a mathematical framework based on screw theory to solve the kine- matics and dynamics of an arbitrary open chain manipulator. The configuration of two specific manipulators is described in this framework as an example. For one of the manipulators, a anthropomorphic 7 DoF arm, a closed form solution of the inverse kinematics … Read More “JournalClub: Mathematical Framework for Arbitrary Open Chain Manipulators” »
Objective. Brain–machine interface (BMI) technologies have succeeded in controlling robotic exoskeletons, enabling some paralyzed people to control their own arms and hands. We have developed an exoskeleton asynchronously controlled by EEG signals. In this study, to enable real-time control of the exoskeleton for paresis, we developed a hybrid system with EEG and EMG signals, and … Read More “JournalClub: A hybrid BMI-based exoskeleton for paresis: EMG control for assisting arm movements” »
In this paper we argue for the fundamental importance of the value distribution: the distribution of the random return received by a reinforcement learning agent. This is in contrast to the common approach to reinforcement learning which models the expectation of this return, or value. Although there is an established body of literature studying the … Read More “JournalClub: A Distributional Perspective on Reinforcement Learning” »
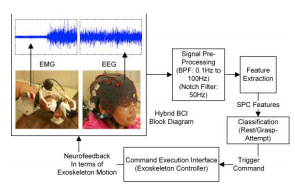
Traditionally a Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) system uses Electroencephalogram (EEG) signals for communication and control applications. In recent years different biological signals are also combined with EEG signals to produce hybrid BCI devices to overcome the limitation of lower accuracy rates in BCI. This paper presents a new approach of combining EEG and Electromyogram (EMG) signals … Read More “JournalClub: EEG-EMG based Hybrid Brain Computer Interface for Triggering Hand Exoskeleton for Neuro-Rehabilitation” »
In this paper, a novel self-organizing fuzzy neural network is proposed that constructed by an input–output mapping and monitored by a hierarchy of validity degrees. We define new operators called validification and devalidification to propagate validity into the six layers of proposed architecture. Self-organizing in structure learning is accomplished through a new measure that depends … Read More “JournalClub: Introducing validity into self-organizing fuzzy neural network applied to impedance force control” »
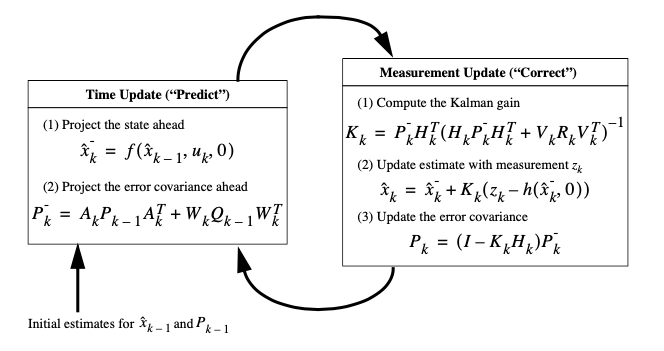
In statistics and control theory, Kalman filtering, also known as linear quadratic estimation (LQE), is an algorithm that uses a series of measurements observed over time, containing statistical noise and other inaccuracies, and produces estimates of unknown variables that tend to be more accurate than those based on a single measurement alone, by estimating a … Read More “JournalClub: An Introduction to Kalman Filter” »
The continuous control of rehabilitation robots based on surface electromyography (sEMG) isa natural control strategy that can ensure human safety and ease the discomfort of human-machine coupling.However, current models for estimating movement of the upper limb focus on two dimensions movement,and models of three dimensions movement are too complex. In this paper, a simple-structure temporalinformation-based … Read More “JournalClub: A Continuous Estimation Model of Upper Limb Joint Angles by Using Surface Electromyography and Deep Learning Method” »
Objective: Stroke is a leading cause of long-term motor disability. Stroke patients with severe hand weakness do not profit from rehabilitative treatments. Recently, brain-controlled robotics and sequential functional electrical stimulation allowed some improvement. However, for such therapies to succeed, it is required to decode patients’ intentions for different arm movements. Here, we evaluated whether residual … Read More “Decoding upper limb residual muscle activity in severe chronic stroke” »
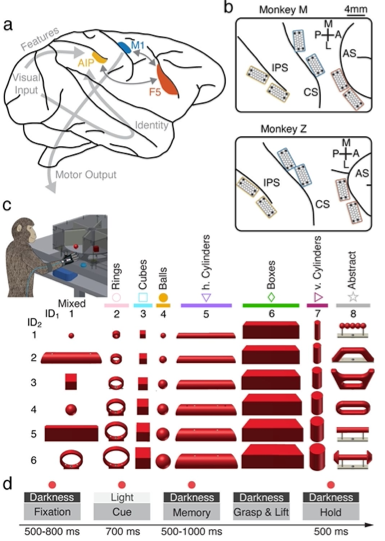
One of the primary ways we interact with the world is using our hands. In macaques, the circuitspanning the anterior intraparietal area, the hand area of the ventral premotor cortex, and the primarymotor cortex is necessary for transforming visual information into grasping movements. Wehypothesized that a recurrent neural network mimicking the multi-area structure of the … Read More “JournalClub: A neural network model of flexible grasp movement generation” »
Error-related potentials are the neural signature of the error processing in the brain. These event-related potentials can be measured via Electroencephalography (EEG) and are present upon both self-made as well as other’s errors. In our project we are interested in the applications of such signals in brain-computer interfaces. Presented on 03.03.2021 (Aline Xavier Fidêncio) Links: … Read More “ProgressClub: On the application of error-related potentials” »