Student project within the module “Autonomous Systems” at Ruhr West University of Applied Sciences. Students Tim Büttel, Jonas Peltzer, Pierre Pospiech, Jannik Schremmern Supervision Tim Sziburis, Susanne Blex, Felix Grün, Prof. Dr. Ioannis Iossifidis Project site https://gitlab.hs-ruhrwest.de/iSystemsStudentProjects/2020/eeg-emg-gamecontroller
Category: teaching
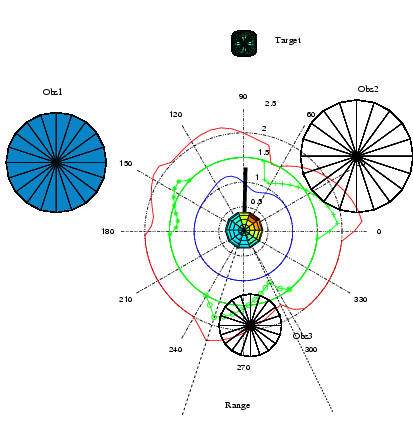
Student project within the module “Autonomous Systems” at Ruhr West University of Applied Sciences. Students Marvin Maciejewski, Stefan Fohs, Tristan Rienow Supervision Prof. Dr. Ioannis Iossifidis Project site https://gitlab.hs-ruhrwest.de/iSystemsStudentProjects/2020/eeg-emg-gamecontroller live demo
Student project within the module “Autonomous Systems” at Ruhr West University of Applied Sciences. Students Philipp Lösch, Lars Telöken, Ralf Wenzel, Alex Wichmann Supervision Prof. Dr. Ioannis Iossifidis Project site https://gitlab.hs-ruhrwest.de/iSystemsStudentProjects/2020/eeg-emg-gamecontroller live demo
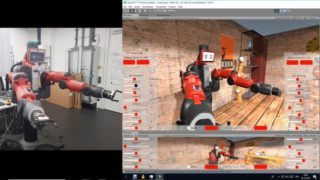
The robot Baxter ist modeled in Unity3D and a UDP interface is implemented for multi process communication. The UDP interface connects also the real robot with the VR-Robot and can be used to either execute learn motion in the VR on the real robot or just to monitor in the VR the executed movements of … Read More “VR Simulation of Baxter” »
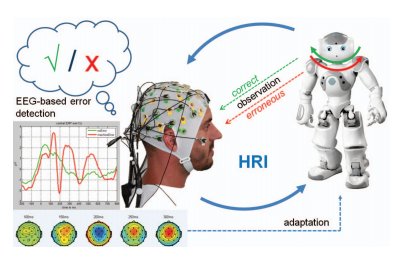
Validating appropriateness and naturalness of human-robot interaction (HRI) is commonly performed by taking subjective measures from human interaction partners, e.g. questionnaire ratings. Although these measures can be of high value for robot designers, they are very sensitive and can be inaccurate and/or biased. In this paper we propose and validate a neuro-based method for objectively … Read More “JournalClub: A neuro-based method for detecting context-dependent erroneous robot action” »
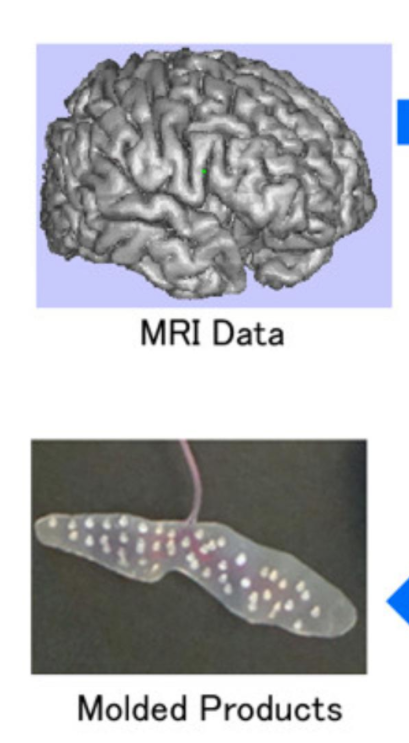
Brain–machine interfaces (BMIs) are promising devices that can be used as neuroprostheses by severely disabled individuals. Brain surface electroencephalograms (electrocorticograms, ECoGs) can provide input signals that can then be decoded to enable communication with others and to control intelligent prostheses and home electronics. However, conventional systems use wired ECoG recordings. Therefore, the development of wireless … Read More “JournalClub: A Fully Implantable Wireless ECoG 128Channel Recording Device for Human Brain–Machine Interfaces” »
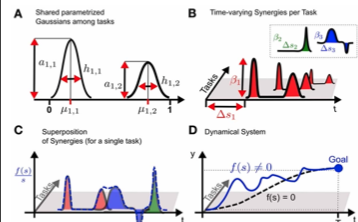
A salient feature of human motor skill learning is the ability to exploit similarities across related tasks. In biological motor control, it has been hypothesized that muscle synergies, coherent activations of groups of muscles, allow for exploiting shared knowledge. Recent studies have shown that a rich set of complex motor skills can be generated by … Read More “JournalClub: Learned parametrized dynamic movement primitives with shared synergies for controlling robotic and musculoskeletal systems” »
Error-related potentials (ErrPs) are the neural signature of error processing. Therefore, the detectionof ErrPs is an intuitive approach to improve the performance of brain-computer interfaces (BCIs). The incorporation of ErrPs in discrete BCIs is well established but the study of asynchronous detection of ErrPs is still in its early stages. Here we show the feasibility … Read More “JournalClub: Online asynchronous decoding of error-related potentials during the continuous control of a robot” »
Movement primitives are elementary motion units and can be combined sequentially or simultaneously to compose more complex movement sequences. A movement primitive timeseries consist of a sequence of motion phases. This progression through a set of motion phases can be modeled by Hidden Markov Models (HMMs). HMMs are stochastic processes that model time series data … Read More “JournalClub: Modeling Movement Primitives with Hidden Markov Models for Robotic and Biomedical Applications” »
This work has been conducted in the context of pattern-recognition-based control strategies for electromyographic prostheses. It focuses on the conceptual design, implementation and validation of learning techniques based on the k-nearest neighbour (kNN) scheme for gesture recognition. After theoretical considerations and the identification of the topic within the contexts of prosthetic control, biomedical signals — … Read More “JournalClub: Nearest-Neighbour-Based Learning Techniques for Proportional Myocontrol in Prosthetics” »