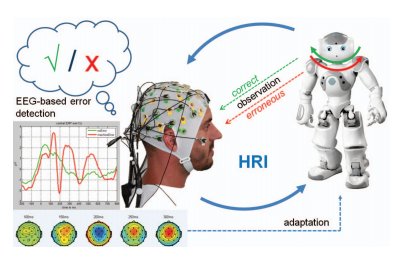
Validating appropriateness and naturalness of human-robot interaction (HRI) is commonly performed by taking subjective measures from human interaction partners, e.g. questionnaire ratings. Although these measures can be of high value for robot designers, they are very sensitive and can be inaccurate and/or biased. In this paper we propose and validate a neuro-based method for objectively … Read More “JournalClub: A neuro-based method for detecting context-dependent erroneous robot action” »
Brain–machine interfaces (BMIs) are promising devices that can be used as neuroprostheses by severely disabled individuals. Brain surface electroencephalograms (electrocorticograms, ECoGs) can provide input signals that can then be decoded to enable communication with others and to control intelligent prostheses and home electronics. However, conventional systems use wired ECoG recordings. Therefore, the development of wireless … Read More “JournalClub: A Fully Implantable Wireless ECoG 128Channel Recording Device for Human Brain–Machine Interfaces” »
JournalClub: Navigating features: a topologically informed chart of electromyographic features space
The success of biological signal pattern recognition depends crucially on the selection of relevant features. Across signal and imaging modalities, a large number of features have been proposed, leading to feature redundancy and the need for optimal feature set identification. A further complication is that, due to the inherent biological variability, even the same classification … Read More “JournalClub: Navigating features: a topologically informed chart of electromyographic features space” »
1.Human muscle fatigue has been studied using a wide variety of exercise models, protocols and assessment methods. Based on the definition of fatigue as ‘any reduction in the maximal capacity to generate force or power output’, the different methods to measure fatigue are discussed. It is argued that reliable and valid measures must include either … Read More “ProgressClub: Muscle Fatigue” »
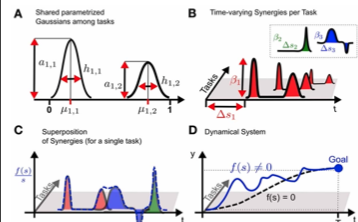
A salient feature of human motor skill learning is the ability to exploit similarities across related tasks. In biological motor control, it has been hypothesized that muscle synergies, coherent activations of groups of muscles, allow for exploiting shared knowledge. Recent studies have shown that a rich set of complex motor skills can be generated by … Read More “JournalClub: Learned parametrized dynamic movement primitives with shared synergies for controlling robotic and musculoskeletal systems” »
Presented on 30.09.2020 by Sebastian Doliwa
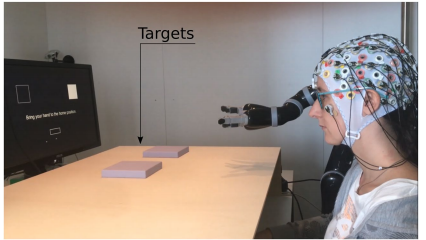
Error-related potentials (ErrPs) are the neural signature of error processing. Therefore, the detectionof ErrPs is an intuitive approach to improve the performance of brain-computer interfaces (BCIs). The incorporation of ErrPs in discrete BCIs is well established but the study of asynchronous detection of ErrPs is still in its early stages. Here we show the feasibility … Read More “JournalClub: Online asynchronous decoding of error-related potentials during the continuous control of a robot” »
Presented on 09.09.2020 by Stephan Lehmler
Presented on 26.08.2020 by Felix Grün
Presented on 12.08.2020 by Marie Schmidt