Investigation of the Interplay of Model-Based and Model-Free Learning Using Reinforcement Learning The reward prediction error hypothesis of dopamine in the brain states that activity of dopaminergic neurons in certain brain regions correlates with the reward prediction error that corresponds to the temporal difference error, often used as a learning signal in model free reinforcement … Read More “BCCN23: Investigation of the Interplay of Model-Based and Model-Free Learning Using Reinforcement Learning” »
Category: scientific publication
Iossifidis Lab is participating with 4 publications at the Bernstein Conference 2023 in Berlin. Meet us from 27.09 to 29.09.2023 at the Humboldt Universität zu Berlin and Charité
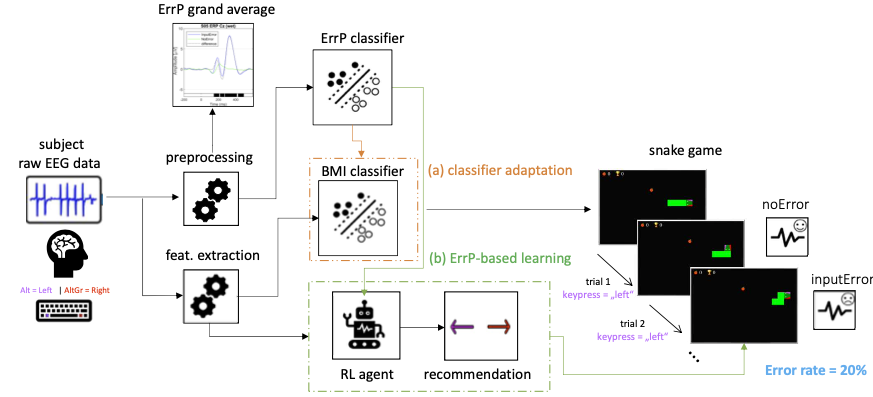
Non-invasive techniques like EEG can record error-related potentials (ErrPs), neural signals associated with error processing and awareness. ErrPs are generated in response to self-made and external errors, including those produced by the BMI. Since ErrPs are implicitly elicited and don’t add extra workload for the subject, they serve as a natural and intrinsic feedback source … Read More “BCCN23: Exploring Error-related Potentials in Adaptive Brain-Machine Interfaces: Challenges and Investigation of Occurrence and Detection Ratios” »
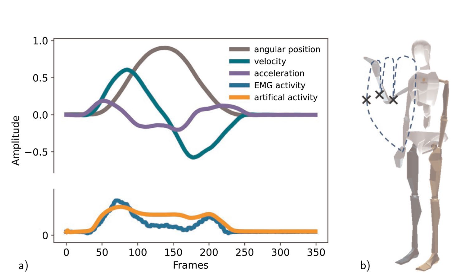
Published at BioMedical Engineering OnLineMarie D. Schmidt*, Tobias Glasmachers and Ioannis Iossifidis Abstract Background: The underlying motivation of this work is to demonstrate that artificial muscle activity of known and unknown motion can be generated based on motion parameters, such as angular position, acceleration, and velocity of each joint (or the end-effector instead), which are similarly represented … Read More “The concepts of muscle activity generation driven by upper limb kinematics” »
Closed-loop adaptation of brain-machine interfaces using error-related potentials and reinforcement learning Aline Xavier Fidêncio1, 2, 3 , Christian Klaes1 , Ioannis Iossifidis2 University Hospital Knappschaftskrankenhaus, Ruhr University Bochum, Bochum, Germany Institute of Computer Science, Ruhr West University of Applied Sciences, Mülheim an der Ruhr, Germany Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Information Technology, Ruhr University Bochum, … Read More “Bernstein Conference 2022:Closed-loop adaptation of brain-machine interfaces using error-related potentials and reinforcement learning” »
Marie Dominique Schmidt1 , Ioannis Iossifidis1 Institute of Computer Science, University of Applied Science Ruhr West, Duisburger Str. 100, 45479 Mülheim an der Ruhr, Germany The upper limbs enable us to perform a variety of tasks in everyday life that require strength and a wide range of motion as well as precision. For coordinated motion, … Read More “Bernstein Conference 2022: Linking muscle activity and motion trajectory” »
Felix Grün1, 2 , Muhammed Saif-ur-Rehman1 , Ioannis Iossifidis1 Department for Computer Science, Ruhr-West University of Applied Sciences, Lützowstraße 5, 46236 Bottrop, Germany Institut für Neuroinformatik, Ruhr-University Bochum, Universitätsstraße 150, 44801 Bochum, Germany The relation between the activity of dopaminergic neurons and the temporal difference error in Reinforcement Learning (RL) problems [1] is well-known to … Read More “Bernstein Conference 2022: Exploring Distribution Parameterizations for Distributional Continuous Control” »
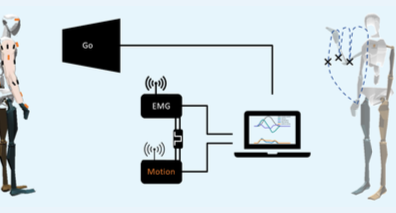
Stephan Johann Lehmler, Muhammad Saif-Ur-Rehman, Ioannis Iossifidis Computer Science, Ruhr West University of Applied Science, 45407 Mülheim an der Ruhr, Germany Institute for Neural Computation, Ruhr-University Bochum, 44801 Bochum, Germany Bioelectrical signals gathered via surface electromyography (sEMG) are the basis of muscle-machine-interfaces (MMI), which makes accurate decoding of those signals an important step in aplications … Read More “Bernstein Conference 2022: Modeling subject specfic surface EMG features by means of deep learning” »
Susanne Blex, Tim Sziburis, Ioannis Iossifidis Department of Computer Science, Ruhr West University of Applied Sciences, 45407 Mülheim an der Ruhr, Germany Institute of Neuroinformatics, Ruhr University Bochum, 44801 Bochum, Germany In our research, we model human upper-limb motion by means of the attractor dynamics approach as a promising candidate for the generation of human-like … Read More “BernsteinConference 2022:A dataset of 3D hand transport trajectories determined by inertial measurements from a single sensor” »
Sebastian Doliwa∗, Andreas Erbsl ̈oh†, Karsten Seidl†‡ and Ioannis Iossifidis∗∗University of Applied Science Ruhr-West, Institute for Computer Science, Mülheim an der Ruhr, Germany†University of Duisburg-Essen, Electronic Components and Circuits, Duisburg, Germany‡Fraunhofer Institute for Microelectronic Circuits and Systems, Duisburg, Germany In the context of the development of an implantable embedded system interfacing brain activity and enabling … Read More “IEEE-Prime: Development of a Scalable Analog Front-End for Brain-Computer Interfaces” »